Irritable Bowel Syndrome, commonly known as IBS, is a prevalent gastrointestinal disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It can be a source of significant discomfort and distress. In this article, we’ll delve into what IBS is, its symptoms, types, potential causes, and available treatments.
Table of Contents
What is IBS?
Irritable Bowel Syndrome, or IBS, is a chronic functional gastrointestinal disorder. It is characterized by a constellation of symptoms related to the digestive system, including abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits. Unlike some other gastrointestinal conditions, IBS doesn’t cause visible damage to the digestive tract but can still significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
Symptoms of IBS
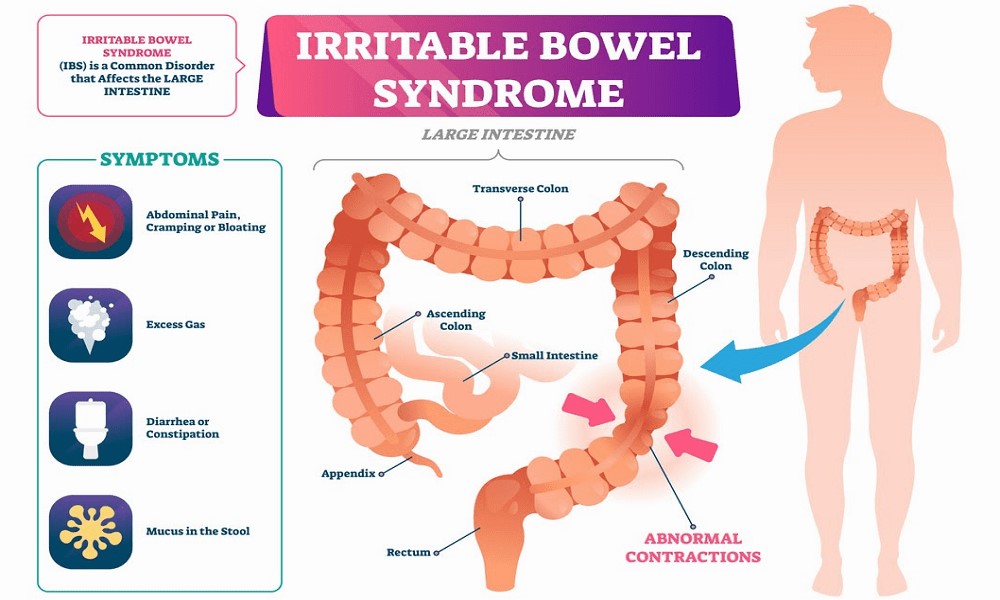
The symptoms of IBS can vary from person to person, but they commonly include:
- Abdominal Pain: Typically, this pain is relieved or partially relieved after a bowel movement.
- Bloating: Many individuals with IBS experience persistent bloating and discomfort.
- Changes in Bowel Habits: This can manifest as diarrhea, constipation, or alternating between both.
- Gas: Excessive gas or flatulence is a common symptom.
- Mucus in Stool: Some people with IBS may notice mucus in their stool.
- Urgency: A sudden and urgent need to have a bowel movement.
- Incomplete Evacuation: A feeling that you haven’t completely emptied your bowels.
Types of IBS
There are three primary types of IBS, categorized based on the predominant bowel habits:
- IBS-D (Diarrhea-Predominant): People with this type of IBS experience frequent diarrhea as a primary symptom.
- IBS-C (Constipation-Predominant): In this type, constipation is the predominant symptom, with infrequent and hard stools.
- IBS-M (Mixed): Individuals with IBS-M experience a combination of diarrhea and constipation.
Causes of IBS
The exact cause of IBS is not fully understood, but several factors may contribute to its development:
- Abnormal Gut Motility: IBS often involves irregular or abnormal contractions of the muscles in the digestive tract, which can lead to changes in bowel habits.
- Visceral Hypersensitivity: Some individuals with IBS have increased sensitivity to pain in their gastrointestinal tract.
- Microbiome: Alterations in the gut microbiome, the community of microorganisms in the digestive system, may play a role in IBS.
- Food Sensitivities: Certain foods and drinks, such as those high in FODMAPs (fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols), can trigger IBS symptoms in susceptible individuals.
- Stress and Psychological Factors: Stress, anxiety, and other psychological factors can exacerbate IBS symptoms.
Treatment for IBS
The management of IBS typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, and, in some cases, medication. Here are some key approaches to managing IBS:
- Dietary Modifications: Identifying and avoiding trigger foods, such as high-FODMAP items, can help alleviate symptoms. Some people with IBS find relief through diets like the low-FODMAP diet.
- Fiber: For those with IBS-C, increasing dietary fiber or taking fiber supplements can help regulate bowel movements.
- Probiotics: Probiotic supplements containing beneficial bacteria may offer relief from certain IBS symptoms.
- Medication: Depending on the specific symptoms, medications like antispasmodics, laxatives, or anti-diarrheal drugs may be prescribed.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as mindfulness, relaxation exercises, and counseling can help manage stress-related IBS symptoms.
- Lifestyle Changes: Regular exercise, adequate sleep, and hydration can contribute to symptom management.
- Prescription Medications: In some cases, prescription medications like lubiprostone or linaclotide may be recommended.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome is a common and often chronic gastrointestinal disorder that affects the daily lives of many individuals. While there is no known cure for IBS, symptom management is possible through dietary adjustments, lifestyle changes, and, if necessary, medication.
If you suspect you have IBS or are experiencing concerning symptoms, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan. With the right approach, individuals with IBS can find relief and regain control of their digestive health.


